The Definitive Debugging Guide for the cert-manager Webhook Pod
Last verified: 8 Sept 2022
The cert-manager webhook is a pod that runs as part of your cert-manager
installation. When applying a manifest with kubectl, the Kubernetes API server
calls the cert-manager webhook over TLS to validate your manifests. This guide
helps you debug communication issues between the Kubernetes API server and the
cert-manager webhook pod.
The error messages listed in this page are encountered while installing or upgrading cert-manager, or shortly after installing or upgrading cert-manager when trying to create a Certificate, Issuer, or any other cert-manager custom resource.
In the below diagram, we show the common pattern when debugging an issue with the cert-manager webhook: when creating a cert-manager custom resource, the API server connects over TLS to the cert-manager webhook pod. The red cross indicates that the API server fails talking to the webhook.
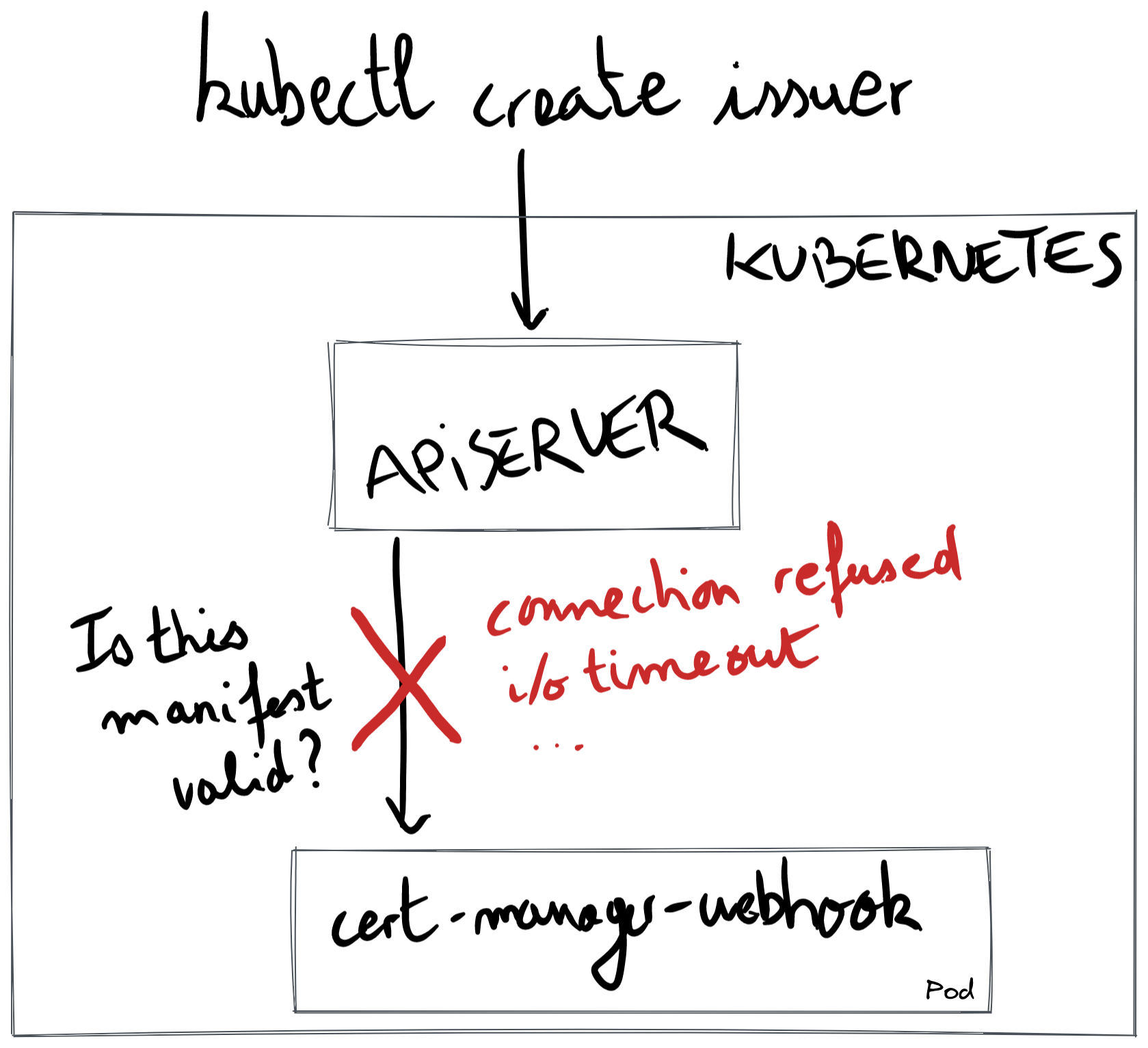
The rest of this document presents error messages you may encounter.
Error: connect: connection refused
This issue was reported in 4 GitHub issues (#2736, #3133, #3445, #4425), was reported in 1 GitHub issue in an external project (
aws-load-balancer-controller#1563), on Stack Overflow (serverfault#1076563), and was mentioned in 13 Slack messages that can be listed with the searchin:#cert-manager in:#cert-manager-dev ":443: connect: connection refused". This error message can also be found in other projects that are building webhooks (kubewarden-controller#110).
Shortly after installing or upgrading cert-manager, you may hit this error when creating a Certificate, Issuer, or any other cert-manager custom resource. For example, creating an Issuer resource with the following command:
kubectl apply -f- <<EOFapiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1kind: Issuermetadata:name: examplespec:selfSigned: {}EOF
shows the following error message:
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN":Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io": failed to call webhook:Post "https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":dial tcp 10.96.20.99:443: connect: connection refused
When installing or upgrading cert-manager 1.5.0 and above with Helm, a very
similar error message may appear when running helm install or helm upgrade:
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: Internal error occurred:failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io": failed to call webhook:Post "https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":dial tcp 10.96.20.99:443: connect: connection refused
The message "connection refused" happens when the API server tries to establish
a TCP connection with the cert-manager-webhook. In TCP terms, the API server
sent the SYN packet to start the TCP handshake, and received an RST packet
in return.
If we were to use tcpdump
inside the control plane node where the API server is running, we would see a
packet returned to the API server:
192.168.1.43 (apiserver) -> 10.96.20.99 (webhook pod) TCP 59466 → 443 [SYN]10.96.20.99 (webhook pod) -> 192.168.1.43 (apiserver) TCP 443 → 59466 [RST, ACK]
The RST packet is sent by the Linux kernel when nothing is listening to the
requested port. The RST packet can also be returned by one of the TCP hops,
e.g., a firewall, as detailed in the Stack Overflow page What can be the
reasons of connection refused errors?
Note that firewalls usually don't return an RST packet; they usually drop the
SYN packet entirely, and you end up with the error message i/o timeout or
context deadline exceeded. If that is the case, continue your investigation
with the section Error: i/o timeout (connectivity issue) and Error: context deadline exceeded respectively.
Let's eliminate the possible causes from the closest to the source of the TCP
connection (the API server) to its destination (the pod cert-manager-webhook).
Let's imagine that the name cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc was resolved
to 10.43.183.232. This is a cluster IP. The control plane node, in which the API
server process runs, uses its iptables to rewrite the IP destination using the
pod IP. That might be the first problem: sometimes, no pod IP is associated with
a given cluster IP because the kubelet doesn't fill in the Endpoint resource
with pod IPs as long as the readiness probe doesn't work.
Let us first check whether it is a problem with the Endpoint resource:
kubectl get endpoints -n cert-manager cert-manager-webhook
A valid output would look like this:
NAME ENDPOINTS AGEcert-manager-webhook 10.244.0.2:10250 27d ✅
If you have this valid output and have the connect: connection refused, then
the issue is deeper in the networking stack. We won't dig into this case, but
you might want to use tcpdump and Wireshark to see whether traffic properly
flows from the API server to the node's host namespace. The traffic from the
host namespace to the pod's namespace already works fine since the kubelet was
already able to reach the readiness endpoint.
Common issues include firewall dropping traffic from the control plane to
workers; for example, the API server on GKE is only allowed to talk to worker
nodes (which is where the cert-manager webhook is running) over port
10250. In EKS, your security groups might deny traffic from your control
plane VPC towards your workers VPC over TCP 10250.
If you see <none>, it indicates that the cert-manager webhook is properly
running but its readiness endpoint can't be reached:
NAME ENDPOINTS AGEcert-manager-webhook <none> 236d ❌
To fix <none>, you will have to check whether the cert-manager-webhook
deployment is healthy. The endpoints stays at <none> while the
cert-manager-webhook isn't marked as healthy.
kubectl get pod -n cert-manager -l app.kubernetes.io/name=webhook
You should see that the pod is Running, and that the number of containers that
are ready is 0/1:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEcert-manager-76578c9687-24kmr 0/1 Running 7 (8h ago) 28d ❌
We won't be detailing the case where you get 1/1 and Running, since it would
indicate an inconsistent state in Kubernetes.
Continuing with 0/1, that means the readiness endpoint isn't answering. When
that happens, no endpoint is created. The next step is to figure out why the
readiness endpoint isn't answering. Let us see which port the kubelet is using
when hitting the readiness endpoint:
kubectl -n cert-manager get deploy cert-manager-webhook -oyaml | grep -A5 readiness
In our example, the port that the kubelet will try to hit is 6080:
readinessProbe:failureThreshold: 3httpGet:path: /healthzport: 6080 # ✨scheme: HTTP
Now, let us port-forward to that port and see if /healthz works. In a shell
session, run:
kubectl -n cert-manager port-forward deploy/cert-manager-webhook 6080
In another shell session, run:
curl -sS --dump-header - 127.0.0.1:6080/healthz
The happy output is:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK ✅Date: Tue, 07 Jun 2022 17:16:56 GMTContent-Length: 0
If the readiness endpoint doesn't work, you will see:
curl: (7) Failed to connect to 127.0.0.1 port 6080 after 0 ms: Connection refused ❌
At this point, verify that the readiness endpoint is configured on that same port. Let us see the logs to check that our webhook is listening on 6080 for its readiness endpoint:
$ kubectl logs -n cert-manager -l app.kubernetes.io/name=webhook | head -10I0607 webhook.go:129] "msg"="using dynamic certificate generating using CA stored in Secret resource"I0607 server.go:133] "msg"="listening for insecure healthz connections" "address"=":6081" ❌I0607 server.go:197] "msg"="listening for secure connections" "address"=":10250"I0607 dynamic_source.go:267] "msg"="Updated serving TLS certificate"...
In the above example, the issue was a misconfiguration of the readiness port. In
the webhook deployment, the argument --healthz-port=6081 was mismatched with
the readiness configuration.
Error: i/o timeout (connectivity issue)
This error message was reported 26 times on Slack. To list these messages, do a search with
in:#cert-manager in:#cert-manager-dev "443: i/o timeout". The error message was reported in 2 GitHub issues (#2811, #4073)
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN": Internal error occurred:failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io": failed to call webhook:Post "https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":dial tcp 10.0.0.69:443: i/o timeout
When the API server tries to talk to the cert-manager webhook, the SYN packet
is never answered, and the connection times out. If we were to run tcpdump
inside the webhook's net namespace, we would see:
192.168.1.43 (apiserver) -> 10.0.0.69 (webhook pod) TCP 44772 → 443 [SYN]192.168.1.43 (apiserver) -> 10.0.0.69 (webhook pod) TCP [TCP Retransmission] 44772 → 443 [SYN]192.168.1.43 (apiserver) -> 10.0.0.69 (webhook pod) TCP [TCP Retransmission] 44772 → 443 [SYN]192.168.1.43 (apiserver) -> 10.0.0.69 (webhook pod) TCP [TCP Retransmission] 44772 → 443 [SYN]
This issue is caused by the SYN packet being dropped somewhere.
Cause 1: GKE Private Cluster
The default Helm configuration should work with GKE private clusters, but
changing securePort might break it.
For context, unlike public GKE clusters where the control plane can freely talk
to pods over any TCP port, the control plane in private GKE clusters can only
talk to the pods in worker nodes over TCP port 10250 and 443. These two open
ports refer to the containerPort inside the pod, not the port called port in
the Service resource.
For it to work, the containerPort inside the Deployment must match either
10250 or 443; containerPort is configured by the Helm value
webhook.securePort. By default, webhook.securePort is set to 10250.
To see if something is off with the containerPort, let us start looking at the
Service resource:
kubectl get svc -n cert-manager cert-manager-webhook -oyaml
Looking at the output, we see that the targetPort is set to "https":
apiVersion: v1kind: Servicemetadata:name: cert-manager-webhookspec:ports:- name: httpsport: 443 # ❌ This port is not the cause.protocol: TCPtargetPort: "https" # 🌟 This port might be the cause.
The reason the above port: 443 can't be the cause is because kube-proxy, which
also runs on the control plane node, translates the webhook's cluster IP to a
pod IP, and also translates the above port: 443 to the value in
containerPort.
To see how what is behind the target port "https", we look at the
Deployment resource:
kubectl get deploy -n cert-manager cert-manager-webhook -oyaml | grep -A3 ports:
The output shows that the containerPort is not set to 10250, meaning that
a new firewall rule will have to be added in Google Cloud.
ports:- containerPort: 12345 # 🌟 This port matches neither 10250 nor 443.name: httpsprotocol: TCP
To recap, if the above containerPort is something other than 443 or 10250 and
you prefer not changing containerPort to 10250, you will have to add a
new firewall rule. You can read the section Adding a firewall rule in a
GKE private
cluster
in the Google documentation.
For context, the reason we did not default securePort to 443 is because
binding to 443 requires one additional Linux capability
(NET_BIND_SERVICE); on the other side, 10250 doesn't require any
additional capability.
Cause 2: EKS on a custom CNI
If you are on EKS and you are using a custom CNI such as Weave or Calico, the Kubernetes API server (which is in its own node) might not be able to reach the webhook pod. This happens because the control plane cannot be configured to run on a custom CNI on EKS, meaning that the CNIs cannot enable connectivity between the API server and the pods running in the worker nodes.
Supposing that you are using Helm, the workaround is to add the following
value in your values.yaml file:
webhook:hostNetwork: truesecurePort: 10260
Or if you are using Helm from the command-line, use the following flag:
--set webhook.hostNetwork=true --set webhook.securePort=10260
By setting hostNetwork to true, the webhook pod will be run in the
host's network namespace. By running in the host's network namespace, the
webhook pod becomes accessible over the node's IP, which means you will
work around the fact that kube-apiserver can't reach any pod IPs nor
cluster IPs.
By setting securePort to 10260 instead of relying on the default value
(which is 10250), you will prevent a conflict between the webhook and the
kubelet. The kubelet, which is an agent that runs on every Kubernetes
worker node and runs directly on the host, uses the port 10250 to
expose its internal API to kube-apiserver.
To understand how hostnetwork and securePort interact, we have to look
at how the TCP connection is established. When the kube-apiserver process
tries to connect to the webhook pod, kube-proxy (which also runs on control
plane nodes, even without a CNI) kicks in and translates the webhook's
cluster IP to the webhook's host IP:
https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/validate||Step 1: resolve to the cluster IPvhttps://10.43.103.211:443/validate||Step 2: send TCP packetvsrc: 172.28.0.1:43021dst: 10.43.103.211:443||Step 3: kube-proxy rewrite (cluster IP to host IP)vsrc: 172.28.0.1:43021dst: 172.28.0.2:10260|| control-plane node| (host IP: 172.28.0.1)------------|--------------------------------------------------| (host IP: 172.28.0.2)v worker node+-------------------+| webhook pod || listens on || 172.28.0.2:10260 |+-------------------+
The reason 10250 is used as the default securePort is because it works
around another limitation with GKE Private Clusters, as detailed in the
above section GKE Private Cluster.
Cause 3: Network Policies, Calico
Assuming that you are using the Helm chart and that you are using the
default value of webhook.securePort (which is 10250), and that you are
using a network policy controller such as Calico, check that there exists a
policy allowing traffic from the API server to the webhook pod over TCP
port 10250.
Cause 4: EKS and Security Groups
Assuming that you are using the Helm chart and that you are using the
default value of webhook.securePort (which is 10250), you might want to
check that your AWS Security Groups allow TCP traffic over 10250 from the
control plane's VPC to the workers VPC.
Other causes
If none of the above causes apply, you will need to figure out why the webhook is unreachable.
To debug reachability issues (i.e., packets being dropped), we advise to
use tcpdump along with Wireshark at every TCP hop. You can follow the
article Debugging Kubernetes Networking: my kube-dns is not
working! to learn
how to use tcpdump with Wireshark to debug networking issues.
Error: x509: certificate is valid for xxx.internal, not cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc (EKS with Fargate pods)
Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:x509: certificate is valid for ip-192-168-xxx-xxx.xxx.compute.internal,not cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc
This issue was first reported in #3237.
This is probably because you are running on EKS with Fargate enabled.
Fargate creates a microVM per pod, and the VM's kernel is used to run the
container in its own namespace. The problem is that each microVM gets its
own kubelet. As for any Kubernetes node, the VM's port 10250 is listened to
by a kubelet process. And 10250 is also the port that the cert-manager
webhook listens on.
But that's not a problem: the kubelet process and the cert-manager webhook process are running in two separate network namespaces, and ports don't clash. That's the case both in traditional Kubernetes nodes, as well as inside a Fargate microVM.
The problem arises when the API server tries hitting the Fargate pod: the
microVM's host net namespace is configured to port-forward every possible port
for maximum compatibility with traditional pods, as demonstrated in the Stack
Overflow page EKS Fargate connect to local kubelet. But the port
10250 is already used by the microVM's kubelet, so anything hitting this port
won't be port-forwarded and will hit the kubelet instead.
To sum up, the cert-manager webhook looks healthy and is able to listen to port
10250 as per its logs, but the microVM's host does not port-forward 10250 to the
webhook's net namespace. That's the reason you see a message about an unexpected
domain showing up when doing the TLS handshake: although the cert-manager
webhook is properly running, the kubelet is the one responding to the API
server.
This is a limitation of Fargate's microVMs: the IP of the pod and the IP of the node are the same. It gives you the same experience as traditional pods, but it poses networking challenges.
To fix the issue, the trick is to change the port the cert-manager webhook is
listening on. Using Helm, we can use the parameter webhook.securePort:
helm install \cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager \--namespace cert-manager \--create-namespace \--version v1.16.0-beta.0 \--set webhook.securePort=10260
Error: service "cert-managercert-manager-webhook" not found
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "test-resources.yaml": Internal error occurred:failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io": failed to call webhook:Post "https://cert-managercert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":service "cert-managercert-manager-webhook" not found
We do not know the cause of this error, please comment on one of the GitHub issues above if you happen to come across it.
Error: no endpoints available for service "cert-manager-webhook" (OVHCloud)
Error: INSTALLATION FAILED: Internal error occurred:failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:no endpoints available for service "cert-manager-webhook"
This issue was first reported once in Slack (1).
This error is rare and was only seen in OVHcloud managed Kubernetes clusters, where the etcd resource quota is quite low. etcd is the database where your Kubernetes resources (such as pods and deployments) are stored. OVHCloud limits the disk space used by your resources in etcd. When the limit is reached, the whole cluster starts behaving erratically and one symptom is that Endpoint resources aren't created by the kubelet.
To verify that it is in fact a problem of quota, you should be able to see the following messages in your kube-apiserver logs:
rpc error: code = Unknown desc = ETCD storage quota exceededrpc error: code = Unknown desc = quota computation: etcdserver: not capablerpc error: code = Unknown desc = The OVHcloud storage quota has been reached
The workaround is to remove some resources such as CertificateRequest resources to get under the limit, as explained in OVHCloud's ETCD Quotas error, troubleshooting page.
Error: x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid
This error message was reported once in Slack (1).
When using kubectl apply:
Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://kubernetes.default.svc:443/apis/webhook.cert-manager.io/v1beta1/mutations?timeout=30s:x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid
This error message was reported once in Slack (1).
Please answer to the above Slack message since we are still unsure as to what may cause this issue; to get access to the Kubernetes Slack, visit https://slack.k8s.io/.
Error: net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN":Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)
This error message was reported once in Slack (1).
Error: context deadline exceeded
This error message was reported in GitHub issues (2319, 2706 5189, 5004), and once on Stack Overflow.
This error appears with cert-manager 0.12 and above when trying to apply an Issuer or any other cert-manager custom resource after having installed or upgraded cert-manager:
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN":Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:context deadline exceeded
ℹ️ In older releases of cert-manager (0.11 and below), the webhook relied on the APIService mechanism, and the message looked a bit different but the cause was the same:
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN":Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.certmanager.k8s.io":Post https://kubernetes.default.svc:443/apis/webhook.certmanager.k8s.io/v1beta1/mutations?timeout=30s:context deadline exceeded
ℹ️ The message
context deadline exceededalso appears when usingcmctl check api. The cause is identical, you can continue reading this section to debug it.Not ready: Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io": failed to call webhook:Post "https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":context deadline exceeded
The trouble with the message context deadline exceeded is that it obfuscates
the part of the HTTP connection that timed out. When this message appears, we
can't tell which part of the HTTP interaction timed out. It might be the DNS
resolution, the TCP handshake, the TLS handshake, sending the HTTP request or
receiving the HTTP response.
ℹ️ For context, the query parameter
?timeout=30sthat you can see in the above error messages is a timeout that the API server decides when calling the webhook. It is often set to 10 or 30 seconds.
The first step to debug this issue is to make sure the timeoutSeconds field on
the cert-manager mutating and validating webhook configurations are
configured to 30 seconds (the maximum value). By default, it is set to 10
seconds, meaning that context deadline exceeded will potentially hide the
other timeout messages. To check the value of the timeoutSeconds field, run:
$ kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations,validatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook \-ojsonpath='{.items[*].webhooks[*].timeoutSeconds}'10 10
This means that both webhooks are configured with a context timeout of 10 seconds. To configure them to 30 seconds, run:
kubectl patch mutatingwebhookconfigurations,validatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook \--type=json -p '[{"op": "replace", "path": "/webhooks/0/timeoutSeconds", "value": 30}]'
The following diagram shows what are the three errors that may be hidden behind
the all-catching context deadline exceeded error message, represented by the
outer box, that is thrown after 30 seconds:
context deadline exceeded|30 seconds |timeout v+-------------------------------------------------------------------------+| || i/o timeout || | net/http: TLS handshake timeout || 10 seconds | | || timeout v | ||------------+ 30 seconds | net/http: request canceled ||TCP | timeout v while awaiting headers ||handshake +---------------------+ | ||------------| TLS | | || | handshake +------------+ 10 seconds | || +---------------------| sending | timeout v || | request +------------+ || +------------|receiving |------+ || |resp. header| recv.| || +------------+ resp.| || | body +-----+| +------|other|| |logic|| +-----++-------------------------------------------------------------------------+
In the rest of the section, we will be trying to trigger one of the three "more specific" errors:
i/o timeoutis the TCP handshake timeout and comes fromDialTimeoutin the Kubernetes apiserver. The name resolution may be the cause, but usually, this message appears after the API server sent theSYNpacket and waited for 10 seconds for theSYN-ACKpacket to be received from the cert-manager webhook.net/http: request canceled while waiting for connection (Client.Timeout exceeded while awaiting headers)is the HTTP response timeout and comes from here and is configured to 30 seconds. The Kubernetes API server already sent the HTTP request is is waiting for the HTTP response headers (e.g.,HTTP/1.1 200 OK).net/http: TLS handshake timeoutis when the TCP handshake is done, and the Kubernetes API server sent the initial TLS handshake packet (ClientHello) and waited for 10 seconds for the cert-manager webhook to answer with theServerHellopacket.
We can sort these three messages in two categories: either it is a connectivity
issue (SYN is dropped), or it is a webhook issue (i.e., the TLS certificate is
wrong, or the webhook is not returning any HTTP response):
| Timeout message | Category |
|---|---|
i/o timeout | connectivity issue |
net/http: TLS handshake timeout | webhook-side issue |
net/http: request canceled while awaiting headers | webhook-side issue |
The first step is to rule out a webhook-side issue. In your shell session, run the following:
kubectl -n cert-manager port-forward deploy/cert-manager-webhook 10250
In another shell session, check that you can reach the webhook:
curl -vsS --resolve cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250:127.0.0.1 \--service-name cert-manager-webhook-ca \--cacert <(kubectl -n cert-manager get secret cert-manager-webhook-ca -ojsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' | base64 -d) \https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250/validate 2>&1 -d@- <<'EOF' | sed '/^* /d; /bytes data]$/d; s/> //; s/< //'{"kind":"AdmissionReview","apiVersion":"admission.k8s.io/v1","request":{"requestKind":{"group":"cert-manager.io","version":"v1","kind":"Certificate"},"requestResource":{"group":"cert-manager.io","version":"v1","resource":"certificates"},"name":"foo","namespace":"default","operation":"CREATE","object":{"apiVersion":"cert-manager.io/v1","kind":"Certificate","spec":{"dnsNames":["foo"],"issuerRef":{"group":"cert-manager.io","kind":"Issuer","name":"letsencrypt"},"secretName":"foo","usages":["digital signature"]}}}}EOF
The happy output looks like this:
POST /validate HTTP/1.1Host: cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250User-Agent: curl/7.83.0Accept: */*Content-Length: 1299Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedHTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Wed, 08 Jun 2022 14:52:21 GMTContent-Length: 2029Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8..."response": {"uid": "","allowed": true}
If the response shows 200 OK, we can rule out a webhook-side issue. Since the
initial error message was context deadline exceeded and not an apiserver-side
issue such as x509: certificate signed by unknown authority or x509: certificate has expired or is not yet valid, we can conclude that the problem
is a connectivity issue: the Kubernetes API server isn't able to establish a TCP
connection to the cert-manager webhook. Please follow the instructions in the
section Error: i/o timeout (connectivity issue) above to
continue debugging.
Error: net/http: TLS handshake timeout
This error message was reported in 1 GitHub issue (#2602).
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN":Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:net/http: TLS handshake timeout
Looking at the above diagram, this error message indicates that the
Kubernetes API server successfully established a TCP connection to the pod IP
associated with the cert-manager webhook. The TLS handshake timeout means that
the cert-manager webhook process isn't the one ending the TCP connection: there
is some HTTP proxy in between that is probably waiting for a plain HTTP request
instead a ClientHello packet.
We do not know the cause of this error. Please comment on the above GitHub issue if you notice this error.
Error: HTTP probe failed with statuscode: 500
This error message was reported in 2 GitHub issue (#3185, #4557).
The error message is visible as an event on the cert-manager webhook:
Warning Unhealthy <invalid> (x13 over 15s) kubelet, node83Readiness probe failed: HTTP probe failed with statuscode: 500
We do not know the cause of this error. Please comment on the above GitHub issue if you notice this error.
Error: Service Unavailable
This error was reported in 1 GitHub issue (#4281)
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "STDIN": Internal error occurred:failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post "https://my-cert-manager-webhook.default.svc:443/mutate?timeout=10s":Service Unavailable
The above message appears in Kubernetes clusters using the Weave CNI.
We do not know the cause of this error. Please comment on the above GitHub issue if you notice this error.
Error: failed calling admission webhook: the server is currently unable to handle the request
This issue was reported in 4 GitHub issues (1369, 1425 3542, 4852)
Error from server (InternalError): error when creating "test-resources.yaml": Internal error occurred:failed calling admission webhook "issuers.admission.certmanager.k8s.io":the server is currently unable to handle the request
We do not know the cause of this error. Please comment in one of the above GitHub issues if you are able to reproduce this error.
Error: x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
Reported in GitHub issues (2602)
When installing or upgrading cert-manager and using a namespace that is not
cert-manager:
Error: UPGRADE FAILED: release core-l7 failed, and has been rolled back due to atomic being set:failed to create resource: conversion webhook for cert-manager.io/v1alpha3, Kind=ClusterIssuer failed:Post https://cert-manager-webhook.core-l7.svc:443/convert?timeout=30s:x509: certificate signed by unknown authority
A very similar error message may show when creating an Issuer or any other cert-manager custom resource:
Internal error occurred: failed calling webhook "webhook.cert-manager.io":Post https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/mutate?timeout=30s:x509: certificate signed by unknown authority`
With cmctl install and cmctl check api, you might see the following error
message:
2022/06/06 15:36:30 Not ready: the cert-manager webhook CA bundle is not injected yet(Internal error occurred: conversion webhook for cert-manager.io/v1alpha2, Kind=Certificate failed:Post "https://<company_name>-cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:443/convert?timeout=30s":x509: certificate signed by unknown authority)
If you are using cert-manager 0.14 and below with Helm, and that you are
installing in a namespace different from cert-manager, the CRD manifest had
the namespace name cert-manager hardcoded. You can see the hardcoded namespace
in the following annotation:
kubectl get crd issuers.cert-manager.io -oyaml | grep inject
You will see the following:
cert-manager.io/inject-ca-from-secret: cert-manager/cert-manager-webhook-ca# ^^^^^^^^^^^^# hardcoded
Note 1: this bug in the cert-manager Helm chart was was fixed in cert-manager 0.15.
Note 2: since cert-manager 1.6, this annotation is no longer used on the cert-manager CRDs since conversion is no longer needed.
The solution, if you are still using cert-manager 0.14 or below, is to render
the manifest using helm template, then edit the annotation to use the correct
namespace, and then use kubectl apply to install cert-manager.
If you are using cert-manager 1.6 and below, the issue might be due to the
cainjector being stuck trying to inject the self-signed certificate that the
cert-manager webhook created and stored in the Secret resource
cert-manager-webhook-ca into the spec.caBundle field of the cert-manager
CRDs. The first step is to check whether the cainjector is running with no
problem:
$ kubectl -n cert-manager get pods -l app.kubernetes.io/name=cainjectorNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEcert-manager-cainjector-5c55bb7cb4-6z4cf 1/1 Running 11 (31h ago) 28d
Looking at the logs, you will be able to tell if the leader election worked. It can take up to one minute for the leader election work to complete.
I0608 start.go:126] "starting" version="v1.8.0" revision="e466a521bc5455def8c224599c6edcd37e86410c"I0608 leaderelection.go:248] attempting to acquire leader lease kube-system/cert-manager-cainjector-leader-election...I0608 leaderelection.go:258] successfully acquired lease kube-system/cert-manager-cainjector-leader-electionI0608 controller.go:186] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/controller/controller-for-secret-customresourcedefinition "msg"="Starting Controller"I0608 controller.go:186] cert-manager/certificate/customresourcedefinition/controller/controller-for-certificate-customresourcedefinition "msg"="Starting Controller"I0608 controller.go:220] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/controller/controller-for-secret-customresourcedefinition "msg"="Starting workers" "worker count"=1I0608 controller.go:220] cert-manager/certificate/customresourcedefinition/controller/controller-for-certificate-customresourcedefinition "msg"="Starting workers" "worker count"=1
The happy output contains lines like this:
I0608 sources.go:184] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/generic-inject-reconciler"msg"="Extracting CA from Secret resource" "resource_name"="issuers.cert-manager.io" "secret"="cert-manager/cert-manager-webhook-ca"I0608 controller.go:178] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/generic-inject-reconciler"msg"="updated object" "resource_name"="issuers.cert-manager.io"
Now, look for any message that indicates that the Secret resource that the cert-manager webhook created can't be loaded. The two error messages that might show up are:
E0608 sources.go:201] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/generic-inject-reconciler"msg"="unable to fetch associated secret" "error"="Secret \"cert-manager-webhook-caq\" not found"
The following message indicates that the given CRD has been skipped because the annotation is missing. You can ignore these messages:
I0608 controller.go:156] cert-manager/secret/customresourcedefinition/generic-inject-reconciler"msg"="failed to determine ca data source for injectable" "resource_name"="challenges.acme.cert-manager.io"
If nothing seems wrong with the cainjector logs, you will want to check that the
spec.caBundle field in the validation, mutation, and conversion configurations
are correct. The Kubernetes API server uses the contents of that field to trust
the cert-manager webhook. The caBundle contains the self-signed CA created by
the cert-manager webhook when it started.
$ kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook -ojson | jq '.webhooks[].clientConfig'{"caBundle": "LS0tLS1...LS0tLS0K","service": {"name": "cert-manager-webhook","namespace": "cert-manager","path": "/validate","port": 443}}
$ kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook -ojson | jq '.webhooks[].clientConfig'{"caBundle": "LS0tLS1...RFLS0tLS0K","service": {"name": "cert-manager-webhook","namespace": "cert-manager","path": "/validate","port": 443}}
Let us see the contents of the caBundle:
$ kubectl get mutatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook -ojson \| jq '.webhooks[].clientConfig.caBundle' -r | base64 -d \| openssl x509 -noout -text -in -Certificate:Data:Version: 3 (0x2)Serial Number:ee:8f:4f:c8:55:7b:16:76:d8:6a:a2:e5:94:bc:7c:6bSignature Algorithm: ecdsa-with-SHA384Issuer: CN = cert-manager-webhook-caValidityNot Before: May 10 16:13:37 2022 GMTNot After : May 10 16:13:37 2023 GMTSubject: CN = cert-manager-webhook-ca
Let us check that the contents of caBundle works for connecting to the
webhook:
$ kubectl -n cert-manager get secret cert-manager-webhook-ca -ojsonpath='{.data.ca\.crt}' \| base64 -d | openssl x509 -noout -text -in -Certificate:Data:Version: 3 (0x2)Serial Number:ee:8f:4f:c8:55:7b:16:76:d8:6a:a2:e5:94:bc:7c:6bSignature Algorithm: ecdsa-with-SHA384Issuer: CN = cert-manager-webhook-caValidityNot Before: May 10 16:13:37 2022 GMTNot After : May 10 16:13:37 2023 GMTSubject: CN = cert-manager-webhook-ca
Our final test is to try to connect to the webhook using this trust bundle. Let us port-forward to the webhook pod:
kubectl -n cert-manager port-forward deploy/cert-manager-webhook 10250
In another shell session, send a /validate HTTP request with the following
command:
curl -vsS --resolve cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250:127.0.0.1 \--service-name cert-manager-webhook-ca \--cacert <(kubectl get validatingwebhookconfigurations cert-manager-webhook -ojson | jq '.webhooks[].clientConfig.caBundle' -r | base64 -d) \https://cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250/validate 2>&1 -d@- <<'EOF' | sed '/^* /d; /bytes data]$/d; s/> //; s/< //'{"kind":"AdmissionReview","apiVersion":"admission.k8s.io/v1","request":{"requestKind":{"group":"cert-manager.io","version":"v1","kind":"Certificate"},"requestResource":{"group":"cert-manager.io","version":"v1","resource":"certificates"},"name":"foo","namespace":"default","operation":"CREATE","object":{"apiVersion":"cert-manager.io/v1","kind":"Certificate","spec":{"dnsNames":["foo"],"issuerRef":{"group":"cert-manager.io","kind":"Issuer","name":"letsencrypt"},"secretName":"foo","usages":["digital signature"]}}}}EOF
You should see a successful HTTP request and response:
POST /validate HTTP/1.1Host: cert-manager-webhook.cert-manager.svc:10250User-Agent: curl/7.83.0Accept: */*Content-Length: 1299Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedHTTP/1.1 200 OKDate: Wed, 08 Jun 2022 16:20:45 GMTContent-Length: 2029Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8...
Error: cluster scoped resource "mutatingwebhookconfigurations/" is managed and access is denied
This message was reported in GitHub issue 3717.
While installing cert-manager on GKE Autopilot, you will see the following message:
Error: rendered manifests contain a resource that already exists. Unable to continue with install:could not get information about the resource:mutatingwebhookconfigurations.admissionregistration.k8s.io "cert-manager-webhook" is forbidden:User "XXXX" cannot get resource "mutatingwebhookconfigurations" in API group "admissionregistration.k8s.io" at the cluster scope:GKEAutopilot authz: cluster scoped resource "mutatingwebhookconfigurations/" is managed and access is denied
This error message will appear when using Kubernetes 1.20 and below with GKE Autopilot. It is due to a restriction on mutating admission webhooks in GKE Autopilot.
As of October 2021, the "rapid" Autopilot release channel has rolled out version 1.21 for Kubernetes masters. Installation via the Helm chart may end in an error message but cert-manager is reported to be working by some users. Feedback and PRs are welcome.
Error: the namespace "kube-system" is managed and the request's verb "create" is denied
When installing cert-manager on GKE Autopilot with Helm, you will see the following error message:
Not ready: the cert-manager webhook CA bundle is not injected yet
After this failure, you should still see the three pods happily running:
$ kubectl get pods -n cert-managerNAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGEcert-manager-76578c9687-24kmr 1/1 Running 0 47mcert-manager-cainjector-b7d47f746-4799n 1/1 Running 0 47mcert-manager-webhook-7f788c5b6-mspnt 1/1 Running 0 47m
But looking at either of the logs, you will see the following error message:
E0425 leaderelection.go:334] error initially creating leader election record:leases.coordination.k8s.io is forbidden: User "system:serviceaccount:cert-manager:cert-manager-webhook"cannot create resource "leases" in API group "coordination.k8s.io" in the namespace "kube-system":GKEAutopilot authz: the namespace "kube-system" is managed and the request's verb "create" is denied
That is due to a limitation of GKE Autopilot. It is not possible to create
resources in the kube-system namespace, and cert-manager uses the well-known
kube-system to manage the leader election. To get around the limitation, you
can tell Helm to use a different namespace for the leader election:
helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --version 1.8.0 \--namespace cert-manager --create-namespace \--set global.leaderElection.namespace=cert-manager
